Introduction
Remote repositories hosted on GitHub have an owner who has the ability to push commits directly to the repo.
TIP
If you created a remote repository, you are the owner.
A select few additional users, at the discretion of the repository owner, may also have the ability to push directly to a remote repository.
However, most often, outside contributors to a repository instead create what is called a fork of a repository.
When someone creates a fork of a repository, they are able to make whatever changes they like to that fork, pushing commits to their fork.
Here is an illustration of this concept:
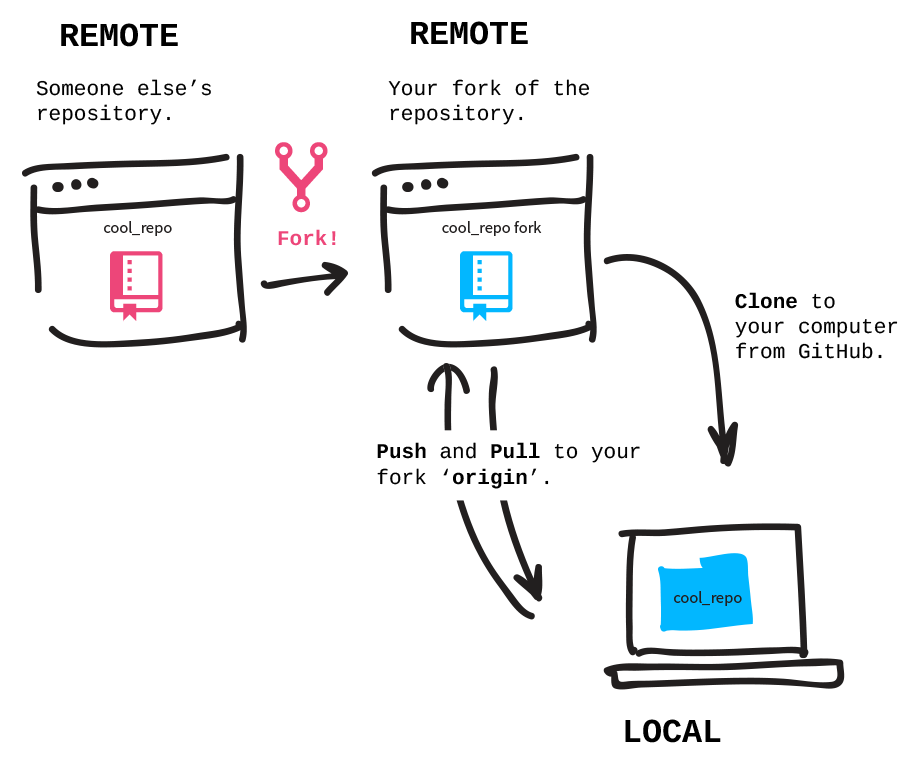
Image credit: Git-it
Here is how to create a fork of a repository on GitHub, in a short 32-second video:
NOTE
Observe, in the video, the username in the top-left corner. At first, it is
lcs-rgordon. That is the original owner of the repository. After that repo is forked, the ownership of the fork is made clear, as the top-left corner now reflects the username of the person who forked the repository:russellgordon.
Cloning
Usually, after creating a fork of a repository, you will want to clone the repo to your computer and open it in Xcode. Here is how to do that: